
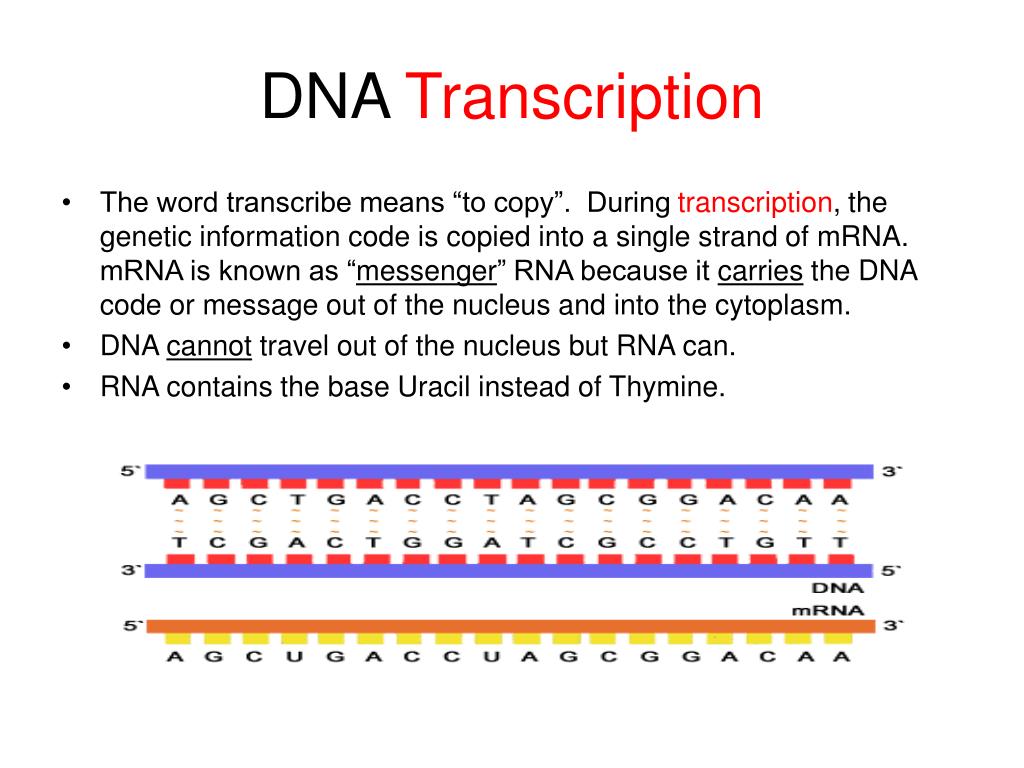
Once the appropriate AUG is identified, the other proteins and CBP dissociate, and the 60S subunit binds to the complex of Met-tRNAi, mRNA, and the 40S subunit. Essentially, the closer the sequence is to this consensus, the higher the efficiency of translation. The R (for purine) indicates a site that can be either A or G, but cannot be C or U. Kozak’s rules state that the following consensus sequence must appear around the AUG of vertebrate genes: 5′-gccRccAUGG-3′. According to Kozak’s rules, the nucleotides around the AUG indicate whether it is the correct start codon.
Many eukaryotic mRNAs are translated from the first AUG, but this is not always the case. Once at the cap, the initiation complex tracks along the mRNA in the 5′ to 3′ direction, searching for the AUG start codon. A cap-binding protein (CBP) and several other IFs assist the movement of the ribosome to the 5′ cap. Instead of depositing at the Shine-Dalgarno sequence, the eukaryotic initiation complex recognizes the 7-methylguanosine cap at the 5′ end of the mRNA. The charged initiator tRNA, called Met-tRNAi, does not bind fMet in eukaryotes, but is distinct from other Met-tRNAs in that it can bind IFs. In eukaryotes, a similar initiation complex forms, comprising mRNA, the 40S small ribosomal subunit, IFs, and nucleoside triphosphates (GTP and ATP). Guanosine triphosphate (GTP), which is a purine nucleotide triphosphate, acts as an energy source during translation-both at the start of elongation and during the ribosome’s translocation. This interaction anchors the 30S ribosomal subunit at the correct location on the mRNA template. coli mRNA, a sequence upstream of the first AUG codon, called the Shine-Dalgarno sequence (AGGAGG), interacts with the rRNA molecules that compose the ribosome. When an in-frame AUG is encountered during translation elongation, a non-formylated methionine is inserted by a regular Met-tRNA Met. coli, but it is usually clipped off after translation is complete. Formylated methionine is inserted by at the beginning of every polypeptide chain synthesized by E. The initiator tRNA interacts with the start codon AUG (or rarely, GUG), links to a formylated methionine called fMet, and can also bind IF-2. coli, this complex involves the small 30S ribosome, the mRNA template, three initiation factors (IFs IF-1, IF-2, and IF-3), and a special initiator tRNA, called. Protein synthesis begins with the formation of an initiation complex.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
